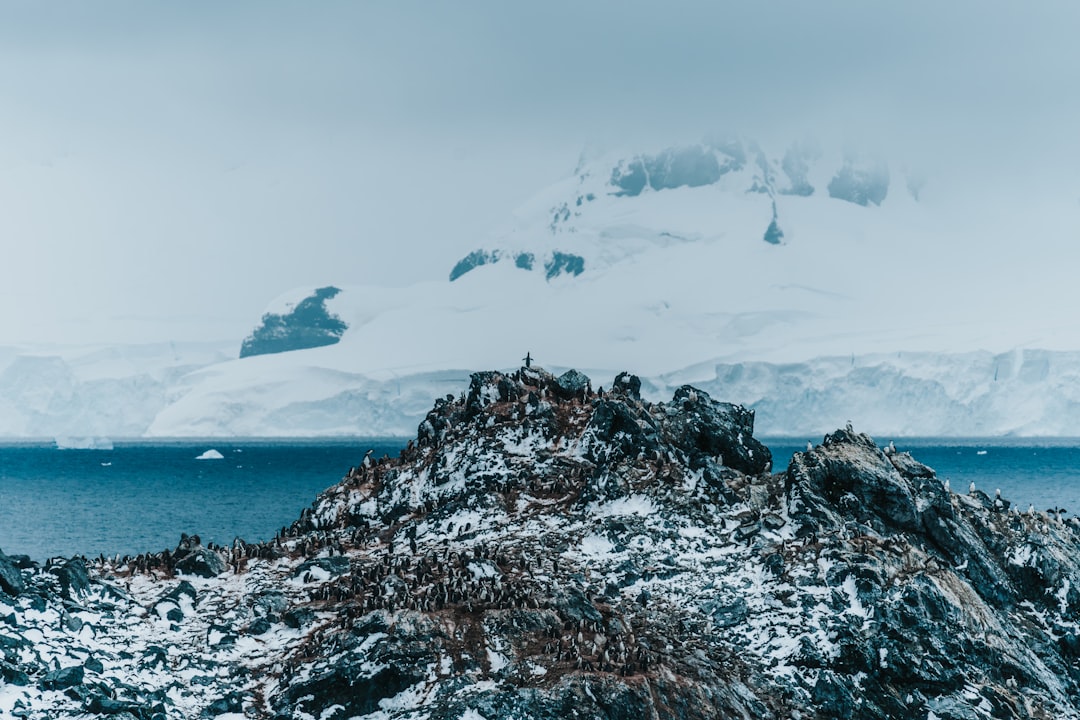
The Drake Passage, a body of water situated between the southern tip of South America and Antarctica, is renowned for its tumultuous seas and significant geographical importance. Spanning approximately 800 kilometers (500 miles) in width, it serves as a critical conduit for ocean currents and marine life. The passage connects the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, playing a vital role in global climate regulation and oceanic circulation.
Its unique position makes it a focal point for researchers and adventurers alike, who are drawn to its unpredictable nature and the mysteries it holds beneath its waves. The waters of the Drake Passage are often characterized by their choppy conditions, which can be attributed to the confluence of various oceanic currents.
This interaction not only influences weather patterns but also affects the biodiversity found within the passage, making it a subject of interest for marine biologists and climatologists.
Key Takeaways
- The Drake Passage is a narrow body of water between South America’s Cape Horn and the South Shetland Islands of Antarctica, known for its rough seas and strong winds.
- The Drake Passage has a significant historical importance as it was first crossed by Sir Francis Drake in 1578, and has since been a key route for explorers and traders.
- Weather conditions in the Drake Passage are characterized by strong winds, high waves, and rapidly changing weather, making it one of the most challenging maritime environments in the world.
- The Drake Passage is home to a diverse range of wildlife, including penguins, seals, whales, and various seabird species, making it a popular destination for wildlife enthusiasts and researchers.
- Navigating the Drake Passage poses significant challenges due to its unpredictable weather, strong currents, and icebergs, requiring skilled and experienced crew and advanced navigation equipment.
- Safety precautions for crossing the Drake Passage include thorough voyage planning, emergency drills, and ensuring the vessel is equipped with appropriate safety gear and communication systems.
- Popular routes through the Drake Passage include the classic Cape Horn route and the more sheltered Beagle Channel route, both offering unique experiences and stunning scenery.
- Tips for a smooth journey through the Drake Passage include packing appropriate clothing for the cold and windy conditions, taking seasickness medication, and staying well-hydrated and rested.
- Notable expeditions and voyages through the Drake Passage include those of Ernest Shackleton, James Cook, and modern-day scientific research expeditions, each contributing to our understanding of the region.
- Environmental concerns in the Drake Passage include the impact of climate change, pollution from maritime traffic, and the need for conservation measures to protect the fragile ecosystem.
- Future developments in navigating the Drake Passage may include advancements in technology for safer and more efficient passage, as well as increased focus on sustainable and eco-friendly practices for maritime travel.
Historical significance of the Drake Passage
Historically, the Drake Passage has been a crucial route for explorers and navigators since the Age of Discovery. Sir Francis Drake, after whom the passage is named, was one of the first Europeans to navigate these treacherous waters in the late 16th century. His voyages contributed significantly to the understanding of global navigation and maritime trade routes.
The passage became a vital link for explorers seeking to reach the southernmost parts of the globe, paving the way for future expeditions to Antarctica and beyond. The significance of the Drake Passage extends beyond exploration; it has also played a pivotal role in maritime trade and military strategy. During the 19th century, whalers and sealers traversed these waters in search of lucrative resources, while naval powers recognized its strategic importance during conflicts.
The passage’s challenging conditions have historically deterred many vessels, yet those who dared to cross have often made remarkable discoveries that have shaped our understanding of geography and oceanography.
Weather conditions in the Drake Passage
The weather conditions in the Drake Passage are notoriously unpredictable, characterized by rapid changes that can occur within a matter of hours. The region is known for its strong winds, high waves, and frequent storms, making it one of the most challenging maritime environments in the world. Sailors often describe the passage as having a “roaring forties” phenomenon, where winds can reach gale force, creating rough seas that test even the most experienced mariners.
Temperature variations also contribute to the passage’s volatile weather patterns. The waters can be frigid, with temperatures often hovering around freezing, especially during winter months. This cold water interacts with warmer air masses from the north, leading to fog, rain, and sudden squalls.
Wildlife in the Drake Passage
| Species | Population | Threat Level |
|---|---|---|
| Antarctic Fur Seal | Unknown | Least Concern |
| Wandering Albatross | Approximately 25,000 breeding pairs | Vulnerable |
| Blue Whale | Unknown | Endangered |
| Antarctic Petrel | Unknown | Least Concern |
The Drake Passage is not only a challenging maritime route but also a rich habitat teeming with diverse wildlife. The nutrient-rich waters support an array of marine life, including various species of fish, seals, and whales. Among the most notable inhabitants are the majestic humpback whales and orcas that migrate through these waters, drawn by abundant food sources such as krill and small fish.
Birdwatchers also flock to the Drake Passage to observe its avian residents. The region is home to numerous seabird species, including albatrosses and petrels, which are often seen gliding gracefully over the waves. These birds play an essential role in the ecosystem, serving as indicators of ocean health and providing insight into environmental changes.
The unique combination of marine life makes the Drake Passage a vital area for ecological research and conservation efforts.
Navigational challenges in the Drake Passage
Navigating the Drake Passage presents numerous challenges due to its unpredictable weather patterns and strong currents. Mariners must contend with shifting winds that can create sudden squalls and towering waves, making it essential for vessels to be equipped with reliable navigation systems and experienced crews. The passage’s narrow width also means that vessels must be particularly cautious when maneuvering through its waters.
In addition to natural obstacles, navigators must be aware of potential hazards such as icebergs and floating debris. The presence of ice can pose significant risks, especially during certain times of the year when icebergs calve from glaciers in Antarctica. Mariners are advised to stay informed about ice conditions and utilize advanced radar technology to detect potential dangers ahead.
Safety precautions for crossing the Drake Passage

Given its reputation for treacherous conditions, safety precautions are paramount when crossing the Drake Passage. Mariners are encouraged to conduct thorough pre-voyage preparations, including checking weather forecasts and ensuring that all safety equipment is in good working order. Life jackets, emergency beacons, and first aid kits should be readily accessible on board.
Additionally, vessels should be equipped with reliable communication systems to maintain contact with other ships and shore-based authorities. In case of emergencies, having a well-trained crew familiar with safety protocols can make a significant difference in ensuring a safe passage through these challenging waters. Regular drills and training sessions can help prepare crew members for potential emergencies they may encounter during their journey.
Popular routes through the Drake Passage
Several popular routes traverse the Drake Passage, catering to both commercial shipping and adventure tourism. One of the most well-known routes is from Ushuaia, Argentina, to various destinations in Antarctica. This journey attracts numerous tourists eager to experience the breathtaking landscapes and unique wildlife of the Antarctic region.
Cruise ships often navigate this route during the summer months when conditions are relatively milder. Another significant route involves research vessels conducting scientific studies in Antarctic waters. These ships play a crucial role in advancing our understanding of climate change and its impact on polar ecosystems.
By traversing the Drake Passage, researchers can access remote areas that are otherwise difficult to reach, allowing them to collect valuable data that informs global environmental policies.
Tips for a smooth journey through the Drake Passage
For those planning a journey through the Drake Passage, several tips can help ensure a smoother experience. First and foremost, travelers should choose their travel dates wisely; late spring to early summer is generally considered the best time for crossing due to more favorable weather conditions. Additionally, selecting a reputable tour operator with experience navigating these waters can enhance safety and comfort.
Packing appropriately is also essential for a successful trip. Travelers should bring layers of clothing suitable for varying temperatures and waterproof gear to stay dry during unexpected rain or splashes from waves. Motion sickness can be a concern for many passengers; therefore, bringing seasickness medication or remedies can help alleviate discomfort during rough crossings.
Notable expeditions and voyages through the Drake Passage
Throughout history, numerous notable expeditions have traversed the Drake Passage, each contributing to our understanding of this remote region. One such expedition was led by Ernest Shackleton in 1914 when he attempted to cross Antarctica via the Weddell Sea. Although his ship became trapped in ice, Shackleton’s remarkable leadership during their harrowing journey back through the Drake Passage has become legendary.
Another significant voyage was undertaken by Robert Falcon Scott during his ill-fated Terra Nova Expedition in 1910-1913. Scott’s team faced immense challenges as they navigated through harsh conditions in pursuit of reaching the South Pole. Their experiences highlighted both the allure and dangers of exploring this remote part of the world.
Environmental concerns in the Drake Passage
As interest in exploring the Antarctic region grows, so do concerns about environmental impacts on the delicate ecosystems within the Drake Passage. Increased shipping traffic poses risks such as oil spills, pollution from waste disposal, and disturbances to marine life due to noise pollution from vessels. Conservationists emphasize the need for sustainable practices to protect this pristine environment from human activities.
Climate change also poses significant threats to the ecosystems within the Drake Passage. Rising ocean temperatures can disrupt marine food chains and lead to shifts in species distribution. Researchers are actively studying these changes to better understand their implications for both local wildlife and global climate patterns.
Future developments in navigating the Drake Passage
Looking ahead, advancements in technology may enhance navigation through the Drake Passage while improving safety measures for vessels traversing these challenging waters. Innovations such as improved weather forecasting models and enhanced radar systems could provide mariners with more accurate information about sea conditions and potential hazards. Furthermore, increased collaboration among nations regarding environmental protection efforts may lead to more stringent regulations governing shipping activities in this sensitive region.
As awareness grows about climate change’s impact on polar ecosystems, there is hope that future developments will prioritize sustainability while allowing safe passage through one of Earth’s most remarkable maritime corridors.
The Drake Passage is a significant body of water that serves as a natural boundary between the southern tip of South America and Antarctica. It is renowned for its challenging navigation conditions due to strong currents and unpredictable weather. For those interested in exploring more about the geographical intricacies and historical significance of the Drake Passage, a related article can be found on MyGeoQuest. This article delves into the passage’s role in global ocean circulation and its impact on maritime travel. To read more, visit the article on MyGeoQuest.
WATCH NOW! Drake Passage: Earth’s Deadliest Waters Revealed
FAQs
What is the Drake Passage?
The Drake Passage is a body of water located between the southern tip of South America and the northern tip of the Antarctic Peninsula. It connects the southwestern part of the Atlantic Ocean with the southeastern part of the Pacific Ocean.
Why is the Drake Passage significant?
The Drake Passage is significant because it represents the shortest and most direct route for oceanic travel between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans in the Southern Hemisphere. It is also known for its notoriously rough and unpredictable seas, making it a challenging and adventurous route for sailors and explorers.
What is the weather like in the Drake Passage?
The weather in the Drake Passage is characterized by strong winds, high waves, and rapidly changing conditions. The area is known for its stormy and turbulent weather, with the potential for extreme cold and rough seas.
What wildlife can be found in the Drake Passage?
The Drake Passage is home to a diverse range of marine wildlife, including various species of whales, dolphins, seals, and seabirds. It is also a popular area for birdwatching, with numerous species of seabirds inhabiting the region.
How is the Drake Passage depicted on maps?
The Drake Passage is typically depicted on maps as a narrow body of water located between South America and Antarctica. It is often labeled with its name and is shown as the primary route for maritime travel between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans in the Southern Hemisphere.
