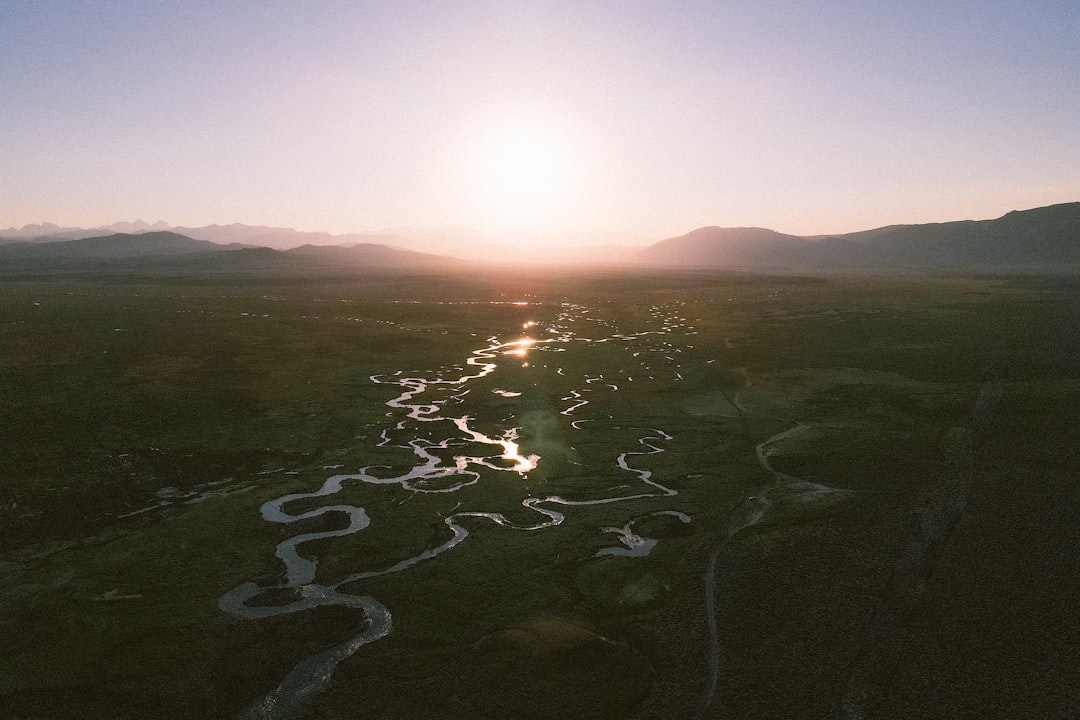
The Drake Passage, a body of water that separates South America from Antarctica, serves as a crucial gateway to the Southern Ocean. This strait is renowned for its turbulent waters and unpredictable weather, making it both a formidable challenge and a vital route for maritime navigation. Stretching approximately 800 kilometers (500 miles) from Cape Horn to the Antarctic Peninsula, the Drake Passage is not only significant for its geographical location but also for its ecological and climatic importance.
It connects the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, allowing for the exchange of marine life and influencing global ocean currents. Navigating the Drake Passage is often described as a rite of passage for sailors and adventurers alike. The waters are notorious for their rough conditions, with waves that can reach heights of over 30 feet.
Despite these challenges, the passage is a popular route for research vessels, cruise ships, and fishing boats, all drawn by the allure of the Southern Ocean’s unique ecosystems and the breathtaking landscapes of Antarctica. The Drake Passage is more than just a stretch of water; it is a dynamic environment that plays a pivotal role in the health of the planet’s oceans.
Key Takeaways
- The Drake Passage is a crucial gateway to the Southern Ocean, connecting the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans.
- Contrary to popular belief, the Drake Passage is not a country, but a significant maritime route.
- The Southern Ocean is a unique and remote region, characterized by its extreme weather and diverse marine life.
- The ecosystem of the Southern Ocean is home to a variety of species, including penguins, seals, and whales.
- The Drake Passage plays a vital role in global climate regulation, influencing ocean currents and atmospheric circulation.
Debunking the Myth: Is Drake Passage a Country?
Despite its prominence in maritime lore, the Drake Passage is not a country. This common misconception may stem from its vastness and significance in global navigation. Some individuals may mistakenly refer to it as a nation due to its historical connections with exploration and discovery.
However, the Drake Passage is simply a geographical feature, a strait that facilitates movement between two major landmasses: South America and Antarctica. The confusion surrounding the status of the Drake Passage can be attributed to its rich history of exploration. Many explorers, including Sir Francis Drake, who is often credited with its name, have traversed these waters in search of new lands and trade routes.
This legacy of exploration has imbued the passage with an air of mystique, leading some to romanticize it as a land unto itself.
The History and Geography of the Southern Ocean
The Southern Ocean, encircling Antarctica, is one of the most remote and least explored oceans on Earth. Its history is intertwined with human exploration, beginning with early navigators who sought to chart its icy waters. The ocean was officially recognized as a distinct body of water in 2000 by the International Hydrographic Organization, although it had been acknowledged by explorers long before that time.
The Southern Ocean is characterized by its cold temperatures, strong currents, and unique marine life, making it a subject of fascination for scientists and adventurers alike. Geographically, the Southern Ocean is defined by its convergence with the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans at the Antarctic Convergence, where cold polar waters meet warmer sub-Antarctic waters. This convergence creates a rich nutrient environment that supports diverse marine ecosystems.
The ocean’s geography is marked by vast ice shelves, deep-sea trenches, and numerous islands, including South Georgia and the South Shetland Islands. These features contribute to its ecological significance and make it a critical area for scientific research.
Exploring the Unique Ecosystem of the Southern Ocean
| Metrics | Value |
|---|---|
| Surface Area | 20.3 million square kilometers |
| Depth | 4,000 to 5,000 meters |
| Unique Species | 10,000 to 12,000 |
| Ice Cover | Approximately 4 million square kilometers |
The Southern Ocean boasts one of the most unique ecosystems on the planet, teeming with life adapted to its frigid waters. It is home to an array of species, including krill, seals, penguins, and various types of whales. Krill, in particular, plays a vital role in this ecosystem as a primary food source for many marine animals.
The abundance of krill supports large populations of predators, creating a complex food web that sustains life in these harsh conditions. In addition to its diverse fauna, the Southern Ocean is characterized by its rich phytoplankton communities that thrive in nutrient-rich waters. These microscopic organisms are essential for carbon cycling and play a crucial role in regulating global climate patterns.
The unique combination of cold temperatures and nutrient availability fosters an environment where life flourishes despite the extreme conditions. Scientists continue to study this remarkable ecosystem to better understand its dynamics and how it may be affected by climate change.
The Importance of the Drake Passage for Global Climate
The Drake Passage plays a significant role in regulating global climate patterns through its influence on ocean currents and heat distribution. The passage facilitates the movement of warm water from the Atlantic Ocean into the Southern Ocean while allowing cold Antarctic waters to flow northward. This exchange is crucial for maintaining the balance of oceanic temperatures and contributes to global climate systems.
Moreover, the Drake Passage acts as a conduit for deep ocean currents that circulate around the globe. These currents are essential for transporting heat and nutrients across vast distances, impacting weather patterns far beyond the Southern Hemisphere. As climate change continues to alter ocean temperatures and currents, understanding the dynamics of the Drake Passage becomes increasingly important for predicting future climate scenarios.
Mythical Lands and Legends: The Origins of the Drake Passage Country Myth

The myth that the Drake Passage could be considered a country may have roots in historical narratives surrounding exploration and discovery. Early explorers often spoke of mythical lands beyond the horizon, fueling imaginations and creating legends about uncharted territories. Sir Francis Drake’s voyages in the late 16th century contributed significantly to this lore; his name became synonymous with adventure and exploration in these treacherous waters.
As tales of exploration spread, so did the idea that vast expanses of ocean could harbor undiscovered lands or nations. This romantic notion persisted through literature and folklore, leading some to mistakenly believe that the Drake Passage itself could be classified as a country. In reality, it remains an open expanse of water that serves as a vital link between continents rather than a sovereign territory.
Scientific Expeditions to the Southern Ocean
Scientific expeditions to the Southern Ocean have been instrumental in advancing knowledge about this remote region. Researchers from around the world embark on voyages to study its unique ecosystems, climate dynamics, and marine biodiversity. These expeditions often involve multidisciplinary teams working together to gather data on everything from oceanographic conditions to wildlife populations.
One notable example is the International Whaling Commission’s research efforts aimed at understanding whale populations in the Southern Ocean. These studies provide valuable insights into how climate change affects marine mammals and their habitats. Additionally, ongoing research into krill populations helps scientists assess the health of this critical species and its role in supporting larger marine ecosystems.
Such expeditions are vital for informing conservation efforts and ensuring sustainable management of resources in this fragile environment.
Protecting the Southern Ocean: Conservation Efforts and Challenges
Conservation efforts in the Southern Ocean face numerous challenges due to its remote location and harsh conditions. Various international agreements aim to protect this unique ecosystem from overfishing, pollution, and climate change impacts. Organizations such as the Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources (CCAMLR) work tirelessly to establish sustainable fishing practices and safeguard marine biodiversity.
However, enforcing these regulations can be difficult given the vastness of the Southern Ocean and limited resources for monitoring activities. Illegal fishing remains a significant threat to marine life in these waters, prompting calls for increased surveillance and enforcement measures. Additionally, climate change poses an existential risk to this delicate ecosystem, necessitating urgent action to mitigate its effects on marine habitats.
The Drake Passage in Literature and Popular Culture
The Drake Passage has captured the imagination of writers and artists throughout history, appearing in various forms of literature and popular culture. Its treacherous waters have been depicted in novels, films, and documentaries that explore themes of adventure, survival, and discovery. The passage’s reputation as one of the most challenging maritime routes has made it a symbol of human resilience against nature’s forces.
In literature, authors have often used the Drake Passage as a backdrop for tales of exploration and adventure. Works such as “The Endurance” by Caroline Alexander recount Ernest Shackleton’s ill-fated expedition across these waters, highlighting both the beauty and peril inherent in navigating this remote region. Similarly, documentaries showcasing wildlife in the Southern Ocean often feature stunning visuals of the passage itself, emphasizing its significance as both a natural wonder and a critical ecological zone.
The Future of Exploration in the Southern Ocean
As technology advances, opportunities for exploration in the Southern Ocean continue to expand. Innovations such as autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) and advanced satellite imaging allow researchers to gather data more efficiently than ever before.
The future of exploration also hinges on international collaboration among scientists from various countries working together to address shared challenges facing the Southern Ocean. By pooling resources and expertise, researchers can conduct comprehensive studies that yield valuable insights into this remote region’s dynamics. As interest in understanding climate change grows globally, so too does recognition of the importance of protecting this unique ecosystem for future generations.
The Fascinating Realities of the Drake Passage and the Southern Ocean
The Drake Passage stands as a testament to nature’s power and beauty while serving as an essential gateway to one of Earth’s most enigmatic regions—the Southern Ocean. While myths may surround its status as a country or harbor hidden lands, its true significance lies in its role within global climate systems and marine biodiversity. As scientific expeditions continue to unveil new discoveries about this remote area, it becomes increasingly clear that protecting its delicate ecosystems is paramount.
Through ongoing conservation efforts and international collaboration among researchers, there is hope for safeguarding this remarkable environment against threats posed by climate change and human activity. The stories woven into literature and popular culture remind us of humanity’s enduring fascination with exploration while highlighting our responsibility to preserve these natural wonders for future generations to appreciate. Ultimately, both the Drake Passage and the Southern Ocean offer profound insights into our planet’s interconnectedness—an intricate tapestry woven from history, science, adventure, and conservation.
The Drake Passage is not a country, but rather a significant body of water located between the southern tip of South America and Antarctica. It is known for its challenging navigation conditions and is a crucial passage for marine biodiversity and global ocean circulation. For those interested in exploring more about geographical features and their significance, you might find this related article on MyGeoQuest insightful. It delves into various geographical phenomena and their impact on our world, providing a broader understanding of how such natural features shape our environment.
WATCH NOW! Drake Passage: Earth’s Deadliest Waters Revealed
FAQs
What is the Drake Passage?
The Drake Passage is a body of water located between the southern tip of South America and the northern tip of the Antarctic Peninsula. It is known for its rough seas and challenging sailing conditions.
Is the Drake Passage a country?
No, the Drake Passage is not a country. It is a maritime region that is part of the Southern Ocean and is not governed by any single country.
What is the significance of the Drake Passage?
The Drake Passage is significant because it is the shortest and most direct route between Antarctica and the rest of the world. It is also an important area for scientific research and exploration.
Are there any countries located in the Drake Passage?
No, there are no countries located in the Drake Passage. The passage is a maritime region and does not contain any landmasses or countries.
What is the climate like in the Drake Passage?
The climate in the Drake Passage is characterized by strong winds, rough seas, and cold temperatures. It is known for its challenging sailing conditions and is often subject to extreme weather.
