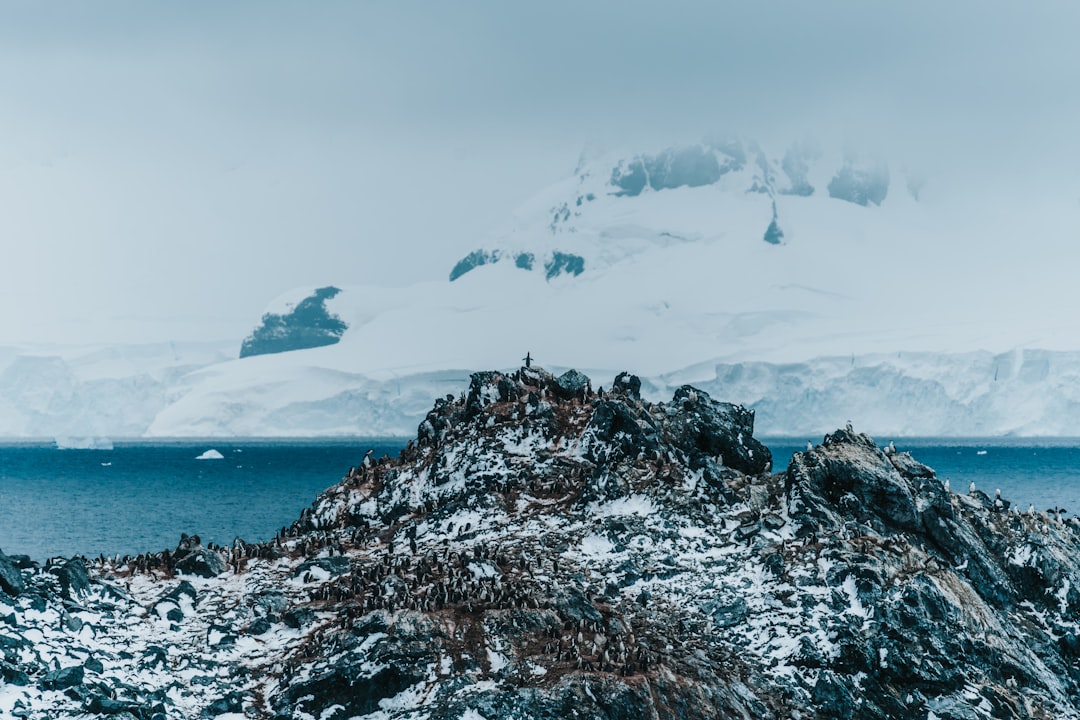
The Drake Passage, a body of water situated between the southern tip of South America and Antarctica, serves as a critical maritime corridor connecting the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. Named after the English explorer Sir Francis Drake, who navigated these treacherous waters in the late 16th century, the passage is renowned for its unpredictable weather and tumultuous seas. Spanning approximately 800 kilometers (500 miles) in width, it is often regarded as one of the most challenging maritime routes in the world.
The passage plays a vital role in global ocean circulation and is a key area for marine biodiversity, making it a focal point for both scientific research and maritime navigation. Navigating the Drake Passage is not for the faint of heart. The waters are notorious for their rough conditions, with waves that can reach heights of over 30 feet during storms.
This unpredictability has earned the passage a reputation among sailors and researchers alike, who must prepare for sudden changes in weather and sea state. Despite these challenges, the Drake Passage remains an essential route for vessels traveling to and from Antarctica, facilitating not only scientific expeditions but also tourism and commercial shipping. Its unique geographical position and ecological significance make it a subject of ongoing interest and study.
Key Takeaways
- The Drake Passage is a narrow stretch of water between South America’s Cape Horn and the South Shetland Islands of Antarctica, known for its turbulent waters and challenging conditions.
- The climate and weather patterns in the Drake Passage are characterized by strong winds, high waves, and rapidly changing conditions, making it one of the roughest seas in the world.
- Oceanographic conditions in the Drake Passage are influenced by the Antarctic Circumpolar Current, creating a unique environment for marine life and research opportunities.
- The Drake Passage is home to a diverse range of wildlife and marine life, including penguins, seals, whales, and various seabird species, making it a popular destination for wildlife enthusiasts and researchers.
- The Drake Passage has been the focus of numerous research and scientific studies, contributing to our understanding of climate change, oceanography, and biodiversity in the region.
Climate and Weather Patterns
The climate of the Drake Passage is characterized by its extreme variability, influenced by the confluence of cold Antarctic waters and warmer currents from the north. This unique interaction creates a dynamic environment where weather patterns can shift rapidly, often within hours. The region experiences strong winds, particularly during the winter months, which can lead to severe storms and high seas.
The average temperature in the passage ranges from -2°C (28°F) in winter to 8°C (46°F) in summer, but these figures can fluctuate dramatically due to changing atmospheric conditions. Precipitation in the Drake Passage is also notable, with frequent rain and snow contributing to the overall moisture levels in the area. The combination of cold air masses from Antarctica and warmer air from the north often results in foggy conditions, further complicating navigation.
Mariners must remain vigilant and well-prepared for sudden weather changes, as visibility can drop quickly, making it difficult to spot other vessels or navigate safely. Understanding these climate patterns is crucial for those who traverse this challenging maritime route.
Oceanographic Conditions
The oceanographic conditions of the Drake Passage are equally complex and fascinating. The passage serves as a significant conduit for ocean currents, particularly the Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC), which flows uninterrupted around Antarctica. This current plays a crucial role in regulating global climate by redistributing heat and nutrients across the oceans.
The interaction between the ACC and other currents creates a rich tapestry of marine environments that support diverse ecosystems. Temperature gradients within the passage can vary significantly, influencing local marine life and nutrient availability. The mixing of cold and warm waters fosters upwelling, which brings nutrient-rich waters to the surface, supporting phytoplankton growth.
This primary production forms the foundation of the food web in the region, attracting various species of fish, seabirds, and marine mammals. Understanding these oceanographic conditions is essential for researchers studying climate change and its impact on marine ecosystems.
Wildlife and Marine Life
| Category | Metrics |
|---|---|
| Wildlife | Number of endangered species |
| Marine Life | Percentage of coral reef coverage |
| Wildlife | Area of protected habitats |
| Marine Life | Population of marine mammals |
The Drake Passage is home to an astonishing array of wildlife and marine life, making it one of the most biodiverse regions on Earth. The nutrient-rich waters support large populations of krill, a small crustacean that serves as a vital food source for many species, including whales, seals, and seabirds. Among the most iconic inhabitants of the passage are various species of whales, such as humpback, minke, and orca whales, which migrate through these waters in search of food during different seasons.
In addition to whales, the passage is teeming with seabirds, including albatrosses and petrels that glide gracefully over the waves. These birds are well adapted to life at sea, often traveling vast distances in search of food. The presence of such diverse wildlife highlights the ecological importance of the Drake Passage as a breeding ground and feeding area for many species.
Conservation efforts are crucial to protect these habitats from human activities that may threaten their delicate balance.
Research and Scientific Studies
The Drake Passage has become a focal point for scientific research due to its unique environmental conditions and ecological significance. Researchers from around the world conduct studies in this region to better understand oceanographic processes, climate change impacts, and marine biodiversity. The passage serves as a natural laboratory for examining how changing temperatures and currents affect marine ecosystems and global climate patterns.
Numerous research expeditions have been launched in the Drake Passage to collect data on water temperature, salinity, and nutrient levels. These studies provide valuable insights into how climate change is altering ocean dynamics and impacting marine life.
The findings from these studies contribute to a broader understanding of global environmental changes and inform conservation strategies aimed at protecting vulnerable marine ecosystems.
Shipping and Navigation Challenges

Navigating the Drake Passage presents significant challenges for shipping and maritime operations. The unpredictable weather patterns, strong currents, and high waves can create hazardous conditions for vessels traversing this route. Mariners must be well-prepared to handle sudden changes in weather and sea state, often relying on advanced technology and navigational tools to ensure safe passage.
The passage is also a critical route for research vessels heading to Antarctica, where scientists conduct important studies on climate change and marine ecosystems. However, the risks associated with navigating these waters necessitate careful planning and coordination among shipping companies, researchers, and regulatory authorities. Ensuring safe navigation through the Drake Passage requires ongoing investment in infrastructure, training for crew members, and adherence to international maritime regulations.
Environmental Concerns
As interest in the Drake Passage grows due to increased shipping traffic and tourism, environmental concerns have come to the forefront. The delicate ecosystems that thrive in these waters are vulnerable to human activities such as overfishing, pollution, and climate change. The introduction of invasive species through ballast water from ships poses an additional threat to native marine life.
Conservation organizations are actively working to raise awareness about the importance of protecting the Drake Passage’s unique environment. Efforts include advocating for sustainable fishing practices, promoting responsible tourism, and supporting research initiatives aimed at understanding the impacts of human activities on marine ecosystems. International cooperation is essential to address these environmental challenges effectively and ensure that future generations can continue to enjoy the natural beauty and biodiversity of this remarkable region.
Historical Significance
The historical significance of the Drake Passage cannot be overstated. It has long been a critical route for explorers, scientists, and mariners seeking to navigate between continents or explore uncharted territories. Sir Francis Drake’s voyages in the late 1500s marked one of the first European encounters with these waters, paving the way for future exploration and trade routes.
Throughout history, the passage has been both a barrier and a bridge for those seeking to reach Antarctica or venture into the Southern Ocean.
These historical journeys have contributed significantly to our understanding of polar regions and have inspired generations of adventurers.
Tourism and Expedition Opportunities
In recent years, tourism in the Drake Passage has surged as more travelers seek adventure in this remote part of the world. Expedition cruises offer opportunities for tourists to experience the breathtaking landscapes of Antarctica while navigating through the passage itself. These journeys often include wildlife watching excursions where passengers can observe whales, seals, and seabirds in their natural habitats.
Tourism operators emphasize responsible practices to minimize environmental impacts while providing unforgettable experiences for travelers. Educational programs on board help raise awareness about the unique ecosystems of the Drake Passage and promote conservation efforts among visitors. As interest in polar tourism continues to grow, balancing economic opportunities with environmental stewardship will be crucial for preserving this pristine region.
International Cooperation and Agreements
Given its ecological significance and strategic importance for global shipping routes, international cooperation is essential for managing activities in the Drake Passage effectively. Various agreements have been established among nations to promote sustainable practices in this region while protecting its unique marine ecosystems. The Antarctic Treaty System serves as a framework for regulating human activities in Antarctica and surrounding waters.
Collaborative research initiatives involving multiple countries have also emerged to address pressing environmental issues such as climate change impacts on marine life. These partnerships facilitate data sharing among scientists working in different disciplines while fostering a sense of shared responsibility for protecting this fragile environment. Continued international cooperation will be vital as challenges related to climate change intensify in the coming years.
Future Outlook and Predictions
Looking ahead, the future of the Drake Passage will be shaped by ongoing environmental changes driven by climate change as well as increasing human activity in this remote region. Scientists predict that rising ocean temperatures could alter current patterns significantly while impacting marine biodiversity within these waters. Additionally, increased shipping traffic may pose new challenges related to pollution management and habitat preservation.
To mitigate potential negative impacts on this vital ecosystem requires proactive measures from governments, researchers, conservationists, industry stakeholders alike—ensuring that sustainable practices are prioritized moving forward. By fostering collaboration among nations while promoting responsible tourism initiatives within this remarkable area—there remains hope that future generations will continue to appreciate all that makes up this extraordinary maritime corridor known as “Drake Passage.”
The Drake Passage, a crucial waterway connecting the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, remains a topic of interest for researchers and adventurers alike due to its challenging conditions and ecological significance. Today, the passage is still known for its unpredictable weather and strong currents, which pose challenges for navigation but also contribute to its rich biodiversity. For those interested in learning more about the current state of the Drake Passage and its impact on global oceanic patterns, a related article can be found on MyGeoQuest. You can explore more about this fascinating region by visiting this page on MyGeoQuest, which provides insights into the geographical and environmental aspects of the Drake Passage.
WATCH NOW! Drake Passage: Earth’s Deadliest Waters Revealed
FAQs
What is Drake Passage?
Drake Passage is the body of water between the southern tip of South America and the northern tip of the Antarctic Peninsula. It is known for its rough seas and challenging sailing conditions.
How is Drake Passage today?
The conditions in Drake Passage can vary greatly from day to day. It is known for its strong winds, large waves, and unpredictable weather. It is always best to check current weather and sea conditions before planning a journey through Drake Passage.
Is it safe to travel through Drake Passage?
While Drake Passage is known for its challenging conditions, many ships and vessels safely navigate through it each year. However, it is important to be prepared for rough seas and adverse weather conditions.
What is the best time to travel through Drake Passage?
The best time to travel through Drake Passage is during the austral summer (November to March) when the weather is relatively milder. However, even during this time, it is important to be prepared for rough seas and strong winds.
Are there any wildlife or natural attractions in Drake Passage?
Drake Passage is known for its rich marine life, including whales, dolphins, and seabirds. It is also a popular route for expedition cruises to Antarctica, offering stunning views of icebergs and glaciers.
