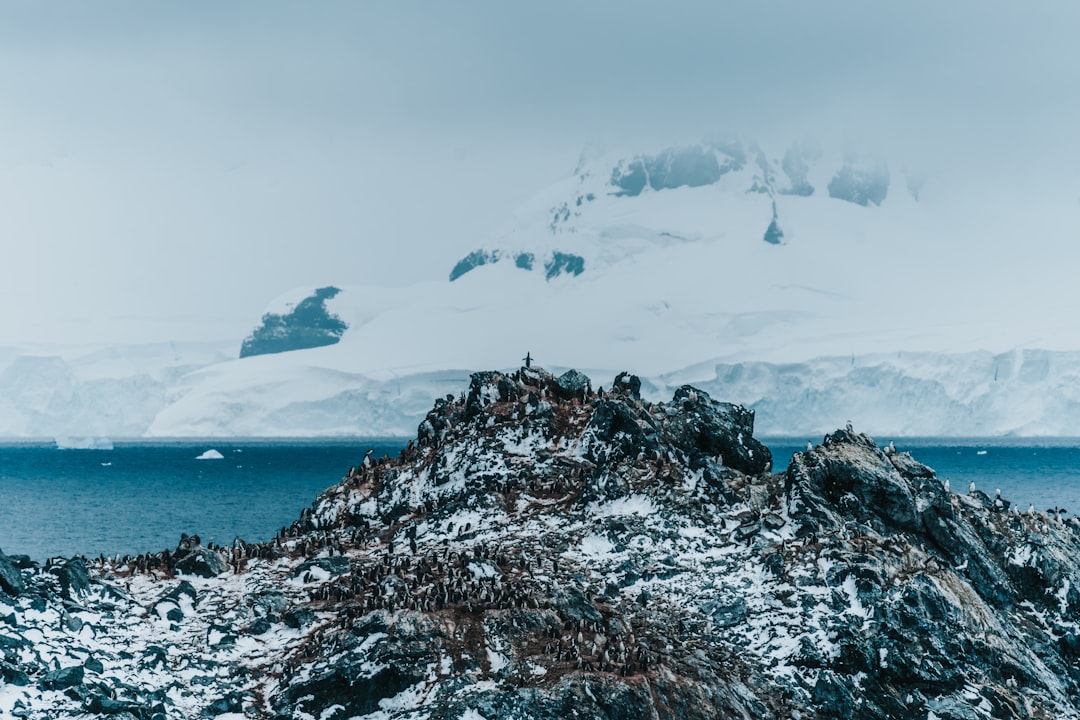
The Drake Passage, a body of water that separates South America from Antarctica, is renowned for its tumultuous seas and unpredictable weather. Stretching approximately 800 kilometers (500 miles) from Cape Horn to the Antarctic Peninsula, this passage is not only a critical maritime route but also a significant ecological zone. The waters of the Drake Passage are often characterized by their rough conditions, which have earned it a reputation as one of the most challenging navigational routes in the world.
Sailors and explorers alike have long been captivated by its beauty and danger, making it a focal point for maritime history and adventure. The passage serves as a vital connection between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, facilitating the movement of ocean currents and marine life.
The Drake Passage is not merely a stretch of water; it is a dynamic environment that plays a crucial role in global climate patterns and marine biodiversity. As such, understanding its significance is essential for appreciating both its natural wonders and its historical context.
Key Takeaways
- The Drake Passage is a body of water between South America’s Cape Horn and the South Shetland Islands of Antarctica.
- Named after Sir Francis Drake, the first Englishman to circumnavigate the globe, the passage has a rich history of exploration and navigation.
- The Drake Passage is a crucial link between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, known for its strong winds and currents, making it a significant geographic feature.
- The passage is home to diverse marine life, including whales, seals, and seabirds, as well as unique flora adapted to the harsh Antarctic environment.
- Early navigators faced immense challenges when crossing the Drake Passage, and modern expeditions and tourism continue to test the limits of exploration in this remote and unpredictable region.
The History of the Name
The name “Drake Passage” pays homage to Sir Francis Drake, the English sea captain and explorer who was the first to navigate these treacherous waters in the late 16th century. His journey, which took place during his circumnavigation of the globe from 1577 to 1580, marked a significant moment in maritime history. Drake’s exploration was not only a testament to his navigational skills but also an indication of the era’s burgeoning interest in exploration and trade.
The passage was named in his honor, reflecting the impact of his voyages on the understanding of global geography. However, the history of the name is not solely tied to Drake. Indigenous peoples, such as the Yaghan and Selk’nam, had long inhabited the regions surrounding the passage long before European explorers arrived.
They referred to these waters with names that reflected their cultural significance and relationship with the land. The juxtaposition of Drake’s name with indigenous nomenclature highlights the complex history of exploration, colonization, and cultural exchange that has shaped the narrative of the Drake Passage.
The Geographic Significance of the Drake Passage
Geographically, the Drake Passage serves as a critical junction between two major oceans: the Atlantic and Pacific. This unique positioning allows for the mixing of oceanic currents, which plays a vital role in regulating global climate patterns. The Antarctic Circumpolar Current flows through this passage, creating a continuous loop that influences weather systems far beyond its immediate vicinity.
This current is essential for maintaining the temperature balance of the Earth’s oceans and is a key factor in climate regulation. Moreover, the Drake Passage is characterized by its deep waters and steep continental shelf, which contribute to its ecological richness. The underwater topography creates diverse habitats that support a wide array of marine life.
The passage’s geographic features not only make it a significant area for navigation but also an important site for scientific research focused on oceanography and climate change. Understanding these geographic dynamics is crucial for comprehending how they affect both local ecosystems and global environmental systems.
The Fauna and Flora of the Drake Passage
| Category | Metrics |
|---|---|
| Marine Mammals | 15 species, including seals and whales |
| Seabirds | More than 20 species, including albatrosses and petrels |
| Flora | Various species of algae and mosses |
| Fish | Several species, including Antarctic toothfish and krill |
The Drake Passage is home to an astonishing variety of marine life, making it one of the most biodiverse regions in the Southern Ocean. The nutrient-rich waters support an array of species, including krill, which serves as a foundational element in the food web. These tiny crustaceans are vital for sustaining larger marine animals such as seals, whales, and seabirds.
The presence of such diverse fauna highlights the ecological importance of the passage and underscores its role as a critical habitat for many species. In addition to its rich marine life, the Drake Passage also boasts unique flora that thrives in its harsh conditions. Algae and phytoplankton flourish in these nutrient-dense waters, forming the basis of the marine food chain.
These organisms not only support local wildlife but also play a significant role in carbon cycling and oxygen production in the ocean.
Exploring the Drake Passage: A Challenge for Early Navigators
For early navigators, traversing the Drake Passage was fraught with peril. The unpredictable weather patterns and turbulent seas posed significant challenges to even the most skilled sailors. Many ships were lost to storms or capsized by towering waves, leading to a reputation that instilled fear in those who dared to navigate these waters.
The passage became synonymous with danger, yet it also represented an opportunity for discovery and adventure. Despite these challenges, explorers were drawn to the allure of the unknown. The quest for new trade routes and territories motivated many to brave the Drake Passage.
Notable figures such as James Cook and Charles Wilkes undertook expeditions that would expand knowledge about Antarctica and its surrounding waters. Their journeys not only contributed to cartographic advancements but also laid the groundwork for future exploration and scientific inquiry in this remote region.
The Importance of the Drake Passage for Scientific Research

The Drake Passage has emerged as a focal point for scientific research due to its unique environmental conditions and ecological significance. Researchers study this area to gain insights into climate change, ocean currents, and marine biodiversity. The passage serves as a natural laboratory where scientists can observe how global warming affects oceanic systems and marine life.
Understanding these dynamics is crucial for predicting future environmental changes and developing strategies for conservation. Moreover, ongoing research in the Drake Passage contributes to broader discussions about ocean health and sustainability. Studies on krill populations, for instance, provide valuable data on how climate change impacts food webs in polar regions.
By examining these ecosystems, scientists can better understand their resilience and vulnerability in the face of environmental stressors. The importance of scientific research in this region cannot be overstated; it plays a vital role in informing policy decisions related to marine conservation and climate action.
Modern Expeditions and Tourism in the Drake Passage
In recent years, modern expeditions have transformed how people experience the Drake Passage. With advancements in technology and navigation, tourists now embark on cruises that traverse these storied waters, offering opportunities to witness breathtaking landscapes and diverse wildlife up close. These expeditions have made it possible for individuals from around the world to explore this remote region while fostering a greater appreciation for its natural beauty.
However, tourism in the Drake Passage comes with its own set of challenges. Increased human activity raises concerns about environmental impacts on fragile ecosystems. Tour operators are increasingly aware of their responsibility to promote sustainable practices that minimize harm to marine life and habitats.
As interest in Antarctic tourism continues to grow, balancing exploration with conservation becomes paramount to preserving the integrity of this unique environment.
Environmental Concerns and Conservation Efforts in the Drake Passage
The ecological significance of the Drake Passage has prompted various conservation efforts aimed at protecting its delicate ecosystems. Environmental concerns have arisen due to climate change, overfishing, and pollution, all of which threaten marine biodiversity in this region. As temperatures rise and ice melts, researchers are closely monitoring changes in species distribution and habitat loss.
Conservation organizations are actively working to raise awareness about these issues while advocating for policies that protect marine environments. Initiatives such as establishing marine protected areas aim to safeguard critical habitats from human exploitation. Collaborative efforts among governments, scientists, and conservationists are essential for ensuring that future generations can continue to appreciate the wonders of the Drake Passage while preserving its ecological integrity.
The Drake Passage in Popular Culture
The Drake Passage has captured the imagination of artists, writers, and filmmakers throughout history, becoming a symbol of adventure and exploration in popular culture. Its treacherous waters have been depicted in literature as a formidable barrier separating civilization from uncharted territories. Films featuring daring voyages often reference this passage as a testament to human resilience against nature’s fury.
Moreover, documentaries showcasing wildlife and environmental issues in the Drake Passage have contributed to public awareness about its significance. These portrayals highlight not only its beauty but also its fragility, encouraging audiences to engage with conservation efforts actively. As popular culture continues to evolve, so too does its representation of this iconic maritime region, reflecting society’s changing relationship with nature.
The Future of Exploration in the Drake Passage
Looking ahead, exploration in the Drake Passage is poised to evolve further as technology advances and scientific inquiry deepens. Innovations such as autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) are enabling researchers to gather data from previously inaccessible areas of this vast oceanic expanse. These tools will enhance understanding of marine ecosystems while providing critical insights into how they respond to environmental changes.
Additionally, as climate change continues to reshape global landscapes, ongoing exploration will be essential for monitoring shifts in biodiversity and habitat health within the Drake Passage. Collaborative international efforts will play a crucial role in addressing these challenges while fostering sustainable practices that prioritize conservation alongside exploration.
The Legacy of the Drake Passage
The legacy of the Drake Passage is multifaceted; it embodies both human ambition and nature’s power. From its historical significance as a navigational challenge to its contemporary role as a site for scientific research and tourism, this body of water continues to inspire awe and respect. As explorers venture into its depths seeking knowledge about our planet’s oceans, they carry forward a tradition rooted in curiosity and discovery.
Ultimately, understanding the complexities surrounding the Drake Passage is vital for appreciating its ecological importance while recognizing our responsibility toward preserving it for future generations. As society grapples with pressing environmental issues, this remarkable passage stands as a reminder of nature’s resilience—a testament to both its beauty and fragility amid an ever-changing world.
The Drake Passage, a significant body of water connecting the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans between the southern tip of South America and Antarctica, is named after the English explorer Sir Francis Drake. This passage is renowned for its challenging navigation conditions and its role in global ocean circulation. For those interested in learning more about the geographical significance and historical context of the Drake Passage, you can explore a related article on the topic by visiting this page. This resource provides further insights into the exploration and naming of this crucial maritime route.
WATCH NOW! Drake Passage: Earth’s Deadliest Waters Revealed
FAQs
What is Drake Passage named after?
Drake Passage is named after Sir Francis Drake, an English sea captain and privateer who is known for being the first Englishman to circumnavigate the globe.
Who was Sir Francis Drake?
Sir Francis Drake was an English sea captain, privateer, and explorer who lived during the 16th century. He is best known for his circumnavigation of the globe and his involvement in the defeat of the Spanish Armada.
Why is Drake Passage named after Sir Francis Drake?
Drake Passage is named after Sir Francis Drake because he was the first Englishman to navigate the treacherous waters of the passage during his circumnavigation of the globe in the late 16th century.
Where is Drake Passage located?
Drake Passage is located between the southern tip of South America (Cape Horn) and the South Shetland Islands of Antarctica. It is a narrow body of water that connects the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans.
What is the significance of Drake Passage?
Drake Passage is significant because it is one of the most challenging and unpredictable bodies of water for maritime navigation. It is known for its strong winds, rough seas, and extreme weather conditions, making it a crucial route for understanding global ocean circulation and climate patterns.
