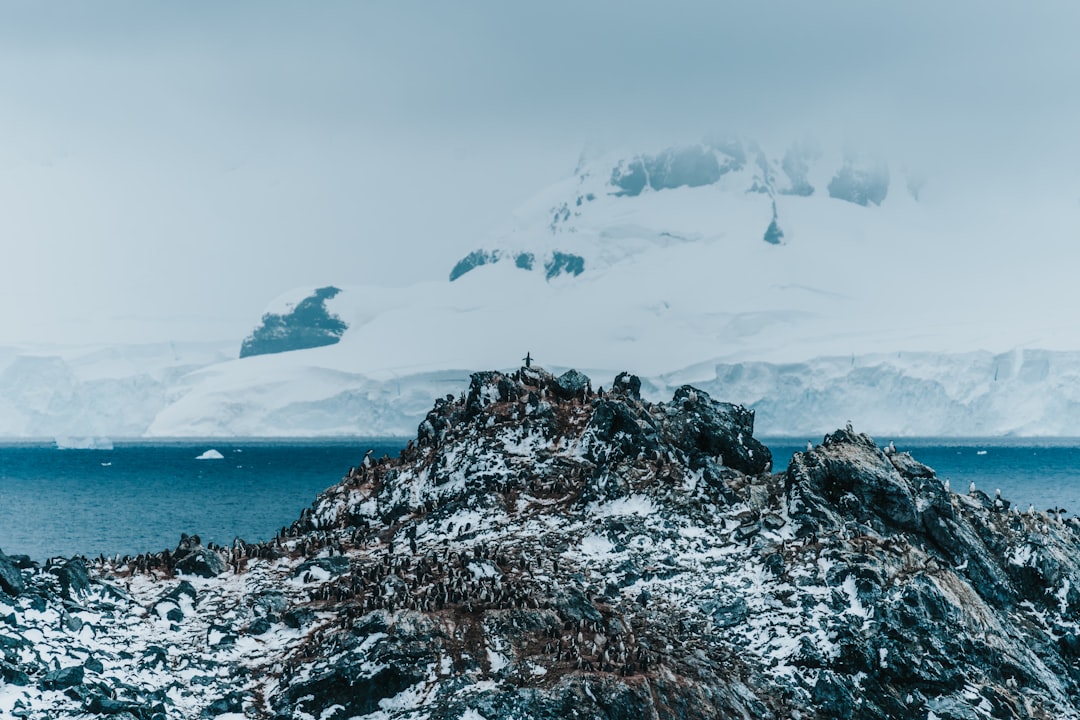
The Drake Passage, a body of water that separates South America from Antarctica, is renowned for its tumultuous seas and rich marine biodiversity. Named after the English explorer Sir Francis Drake, who navigated these waters in the late 16th century, the passage has become a focal point for both scientific research and adventurous exploration. Its unique geographical and ecological characteristics make it a significant area of interest for oceanographers, biologists, and environmentalists alike.
The passage serves as a gateway to the Southern Ocean and is often regarded as one of the most challenging maritime routes in the world. The Drake Passage is not merely a geographical feature; it embodies the intersection of human curiosity and the natural world’s raw power. The waters here are known for their unpredictable weather patterns and strong currents, which can create treacherous conditions for vessels traversing the area.
Despite these challenges, the passage has become a popular route for expedition cruises, drawing tourists eager to experience its breathtaking landscapes and diverse wildlife. As such, the Drake Passage stands as a testament to both the beauty and peril of nature, inviting exploration while demanding respect.
Key Takeaways
- The Drake Passage is a body of water between South America’s Cape Horn and the South Shetland Islands of Antarctica, known for its turbulent seas and challenging weather conditions.
- It is a significant route for global maritime trade and scientific research expeditions, serving as a crucial link between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans.
- The passage has a rich history of exploration, with notable expeditions by famous explorers such as Sir Francis Drake and Captain James Cook.
- The area is known for its unique weather patterns, including strong winds and large waves, making navigation and safety precautions crucial for ships passing through.
- The Drake Passage is home to diverse marine life, including whales, seals, and seabirds, and plays a crucial role in global climate and ocean currents.
Geographic location and significance
Geographically, the Drake Passage lies between Cape Horn at the southern tip of South America and the Antarctic Peninsula. It spans approximately 800 kilometers (500 miles) in width and connects the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. This strategic location not only makes it a vital maritime route but also plays a crucial role in global ocean circulation.
The passage is often characterized by its deep waters, which can reach depths of over 4,000 meters (13,000 feet), creating a unique underwater landscape that supports a diverse array of marine life. The significance of the Drake Passage extends beyond its geographical features.
This current is essential for regulating temperatures and nutrient distribution in the oceans, making the Drake Passage a key player in the Earth’s climate system. As such, understanding the dynamics of this region is vital for scientists studying climate change and its far-reaching impacts.
Historical significance and exploration
The historical significance of the Drake Passage is deeply intertwined with the Age of Exploration. Sir Francis Drake’s voyage through these waters in 1578 marked one of the first recorded European explorations of the region. His journey not only provided valuable information about the geography of South America but also opened up new trade routes and opportunities for exploration.
The passage became a critical point of interest for subsequent explorers, including James Cook and Charles Wilkes, who sought to map its waters and understand its complexities. Throughout history, the Drake Passage has been both feared and revered by sailors. Its reputation for rough seas has led to numerous accounts of shipwrecks and near disasters, making it a symbol of maritime peril.
However, it has also been a site of significant scientific discovery. The exploration of this region has contributed to advancements in navigation, oceanography, and our understanding of marine ecosystems. The legacy of these early explorers continues to influence modern research and exploration efforts in the Drake Passage today.
Unique weather patterns and challenges
| Weather Pattern/Challenge | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| El Niño/La Niña | Periodic warming/cooling of sea surface temperatures in the Pacific Ocean | Altered precipitation patterns, droughts, floods |
| Polar Vortex | Cold air mass that circulates near the poles, sometimes dipping into lower latitudes | Extreme cold temperatures, winter storms |
| Monsoons | Seasonal wind patterns that bring heavy rainfall to certain regions | Flooding, landslides, agricultural impacts |
| Hurricanes/Typhoons | Intense tropical storms with strong winds and heavy rain | Destructive winds, storm surges, flooding |
The weather patterns in the Drake Passage are notoriously unpredictable, characterized by rapid changes that can occur within hours. The convergence of cold Antarctic air with warmer air from the north creates a volatile atmosphere that can lead to fierce storms and high waves. Sailors navigating these waters must be prepared for sudden shifts in weather conditions, which can pose significant challenges to even the most experienced mariners.
These unique weather patterns are not only a challenge for navigation but also play a crucial role in shaping the marine environment. The mixing of different water temperatures and salinities contributes to nutrient upwelling, which supports a rich ecosystem teeming with life. However, this same volatility can make scientific research difficult, as researchers must contend with harsh conditions while trying to study the delicate balance of life in these waters.
Understanding these weather patterns is essential for both safe navigation and effective conservation efforts in the region.
Marine life and biodiversity
The Drake Passage is home to an astonishing array of marine life, making it one of the most biodiverse regions in the world’s oceans. The nutrient-rich waters support large populations of krill, which serve as a fundamental food source for various species, including whales, seals, and seabirds. The presence of these organisms creates a vibrant ecosystem that attracts researchers and wildlife enthusiasts alike.
Among the notable inhabitants of the Drake Passage are several species of whales, including humpback, minke, and orca whales. These majestic creatures migrate through the passage during certain times of the year, offering spectacular sightings for those fortunate enough to witness them. Additionally, seabirds such as albatrosses and petrels are commonly seen soaring above the waves, taking advantage of the strong winds that characterize this region.
The rich biodiversity found in the Drake Passage underscores its ecological importance and highlights the need for ongoing research and conservation efforts.
Impact on global climate and ocean currents

The Drake Passage plays a pivotal role in global climate regulation through its influence on ocean currents. The Antarctic Circumpolar Current flows through this passage, connecting the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans while facilitating heat exchange between these bodies of water. This current is crucial for maintaining temperature balance across the globe and significantly impacts weather patterns far beyond its immediate vicinity.
Moreover, changes in the dynamics of the Drake Passage can have profound implications for climate change. As global temperatures rise, alterations in ocean currents may lead to shifts in marine ecosystems and weather patterns worldwide. Scientists closely monitor this region to understand how these changes may affect not only local biodiversity but also global climate systems.
The interconnectedness of ocean currents highlights the importance of preserving this unique environment as part of broader efforts to combat climate change.
Navigation and safety precautions
Navigating the Drake Passage requires careful planning and preparation due to its challenging conditions. Mariners must be equipped with up-to-date charts and navigational tools to safely traverse these waters. Understanding local weather patterns is essential; many vessels rely on advanced meteorological forecasts to anticipate changes that could impact their journey.
Safety precautions are paramount when sailing through the Drake Passage. Vessels must be well-maintained and equipped with safety gear such as life rafts, emergency beacons, and communication devices. Crew training is also critical; experienced sailors are trained to handle emergencies that may arise from sudden storms or equipment failures.
By adhering to strict safety protocols and being prepared for unexpected challenges, mariners can navigate this formidable passage with greater confidence.
Notable shipwrecks and disasters
The treacherous nature of the Drake Passage has led to numerous shipwrecks throughout history, some of which have become legendary tales of survival and tragedy. One notable disaster occurred in 1914 when Ernest Shackleton’s ship, the Endurance, became trapped in pack ice while attempting to cross the passage on an expedition to Antarctica. The crew’s harrowing journey to safety has since become an iconic story of resilience against nature’s fury.
Another infamous incident involved the sinking of the passenger liner SS Yarmouth Castle in 1965 due to a fire that broke out while navigating through these perilous waters. Such disasters serve as stark reminders of the dangers inherent in traversing the Drake Passage. They highlight not only the need for improved safety measures but also underscore the importance of respecting nature’s power when venturing into this unpredictable environment.
Research and scientific studies in the area
The Drake Passage has become a focal point for scientific research due to its unique ecological characteristics and role in global climate systems. Researchers from around the world conduct studies aimed at understanding marine biodiversity, ocean currents, and climate change impacts within this region. These investigations often involve extensive fieldwork aboard research vessels equipped with advanced technology for data collection.
One significant area of study involves monitoring krill populations, which are vital to the Southern Ocean’s food web. Scientists analyze factors such as temperature fluctuations and ocean acidity levels to assess how these changes may affect krill abundance and distribution. Additionally, ongoing research into ocean currents helps scientists better understand their role in regulating global climate patterns.
The findings from these studies contribute valuable insights into environmental conservation efforts aimed at protecting this fragile ecosystem.
Tourism and expedition opportunities
In recent years, tourism in the Drake Passage has surged as adventurers seek to experience its breathtaking landscapes and unique wildlife firsthand. Expedition cruises have become increasingly popular, offering travelers an opportunity to explore this remote region while learning about its ecological significance from knowledgeable guides. These tours often include activities such as whale watching, birding excursions, and visits to research stations.
While tourism presents exciting opportunities for exploration, it also raises concerns about environmental impact. Responsible tourism practices are essential to minimize disturbances to local wildlife and ecosystems. Many tour operators emphasize sustainability by adhering to strict guidelines designed to protect marine life while providing visitors with unforgettable experiences in this remarkable part of the world.
Future challenges and conservation efforts
As climate change continues to pose significant threats globally, the Drake Passage faces its own set of challenges that require urgent attention.
Conservation efforts are crucial to safeguarding biodiversity while promoting sustainable practices among industries operating in or near these waters.
Organizations dedicated to marine conservation are actively working to raise awareness about the importance of protecting the Drake Passage’s unique environment. Initiatives include establishing marine protected areas (MPAs) that restrict certain activities such as fishing or shipping within designated zones to preserve critical habitats for marine life. Collaborative efforts among governments, scientists, and conservationists will be essential in addressing future challenges while ensuring that this extraordinary region remains vibrant for generations to come.
In conclusion, the Drake Passage stands as a remarkable intersection of natural beauty, historical significance, and ecological importance. Its unique geographic location influences global climate systems while supporting diverse marine life that captivates researchers and tourists alike. As humanity continues to explore this formidable waterway, it is imperative that we prioritize conservation efforts to protect its delicate ecosystems from emerging threats posed by climate change and human activity.
The Drake Passage is notorious for its treacherous conditions, primarily due to its unique geographical and meteorological features. This narrow body of water, located between the southern tip of South America and Antarctica, is where the Atlantic, Pacific, and Southern Oceans converge, creating a tumultuous environment with strong currents and unpredictable weather. The absence of significant landmasses to break the flow of these oceanic currents results in some of the roughest seas on the planet. For a deeper understanding of the factors contributing to the Drake Passage’s perilous nature, you can explore a related article on MyGeoQuest, which delves into the intricate dynamics of this infamous maritime route.
WATCH NOW! Drake Passage: Earth’s Deadliest Waters Revealed
FAQs
What is the Drake Passage?
The Drake Passage is the body of water between the southern tip of South America and the northern tip of the Antarctic Peninsula. It connects the southwestern part of the Atlantic Ocean with the southeastern part of the Pacific Ocean.
Why is the Drake Passage so treacherous?
The Drake Passage is known for its rough seas and strong winds, making it one of the most challenging and treacherous waterways to navigate. The convergence of the Atlantic, Pacific, and Southern oceans creates powerful currents and unpredictable weather patterns, leading to rough and stormy conditions.
What are the weather conditions like in the Drake Passage?
The weather in the Drake Passage is characterized by strong winds, frequent storms, and rough seas. The area is notorious for its high winds and large waves, which can create hazardous conditions for ships and other vessels.
Are there any other factors that contribute to the treacherous nature of the Drake Passage?
In addition to the challenging weather conditions, the Drake Passage is also known for its icebergs and ice floes, which pose a significant hazard to navigation. The presence of these ice formations, combined with the rough seas and strong winds, makes the passage even more treacherous for ships and other vessels.
How do ships and vessels navigate the treacherous conditions of the Drake Passage?
Ships and vessels that traverse the Drake Passage must be well-equipped to handle the challenging conditions. Many vessels are specially designed to withstand rough seas and high winds, and experienced captains and crew members are essential for navigating the passage safely. Additionally, modern technology, such as advanced navigation systems and weather forecasting, helps to mitigate some of the risks associated with the passage.
