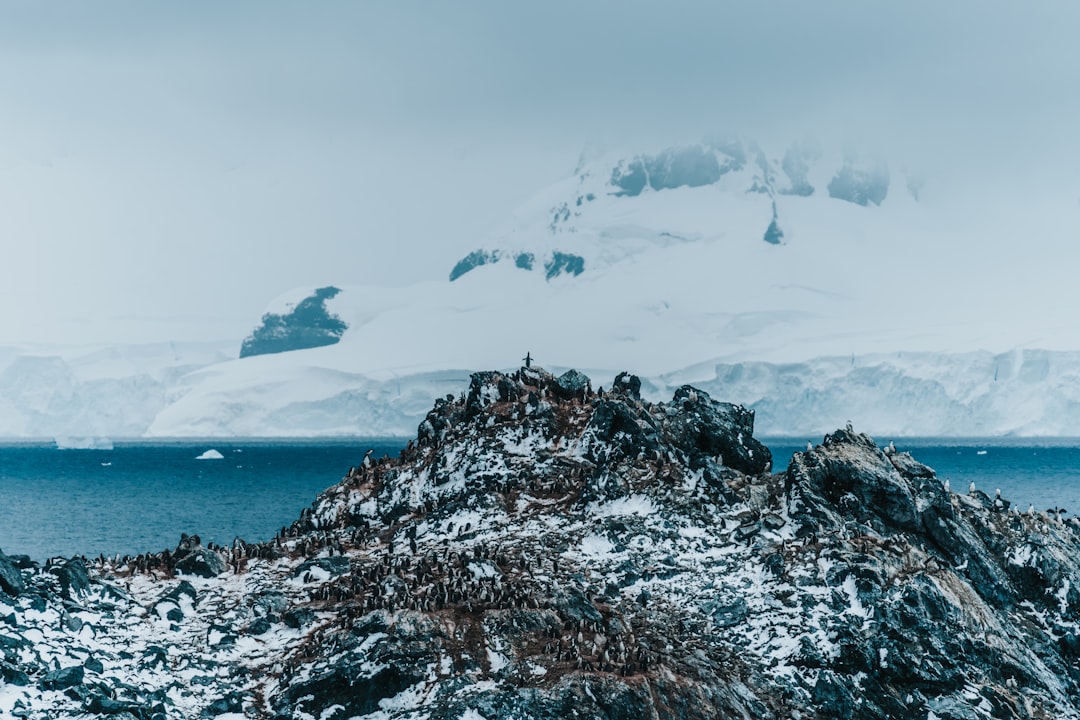
The Drake Passage, a body of water that separates South America from Antarctica, is renowned for its tumultuous seas and unpredictable weather. Named after the English explorer Sir Francis Drake, who navigated these waters in the late 16th century, the passage has become a focal point for maritime exploration and scientific research. Its unique geographical and ecological characteristics make it a significant area of interest for researchers, adventurers, and environmentalists alike.
The allure of the Drake Passage lies not only in its treacherous conditions but also in its rich biodiversity and historical significance. As vessels traverse this stretch of ocean, they encounter a landscape that is both beautiful and formidable.
The passage has become a symbol of adventure, drawing explorers and tourists eager to experience its raw power and natural beauty. Understanding the complexities of the Drake Passage is essential for appreciating its role in global ecology and maritime navigation.
Key Takeaways
- Drake Passage is a narrow body of water between South America’s Cape Horn and the South Shetland Islands of Antarctica.
- It is known for its turbulent waters and challenging weather conditions, making it a significant navigational challenge for ships crossing between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans.
- The passage is home to unique wildlife and marine life, including penguins, seals, and whales, making it a popular destination for wildlife enthusiasts and expedition cruises.
- Drake Passage has historical significance as a route for early explorers and has been the site of important scientific research and discoveries.
- Environmental concerns and conservation efforts are important in the region due to its fragile ecosystem and the impact of climate change.
Geographic Location and Significance
Geographically, the Drake Passage is situated between Cape Horn at the southern tip of South America and the Antarctic Peninsula. It spans approximately 800 kilometers (500 miles) in width, making it one of the narrowest points of oceanic separation between two continents. This strategic location not only influences maritime routes but also plays a crucial role in oceanic currents and climate patterns.
The passage connects the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, facilitating the movement of water masses that are vital for global ocean circulation. The significance of the Drake Passage extends beyond its geographical features. It serves as a critical habitat for various marine species and acts as a conduit for nutrient-rich waters that support diverse ecosystems.
The mixing of warm and cold waters in this region creates a unique environment that fosters biological productivity. As such, the Drake Passage is not only a vital transportation route but also an ecological treasure trove that warrants protection and study.
Climate and Weather Patterns
The climate of the Drake Passage is characterized by its extreme variability, influenced by its position at the convergence of several oceanic currents. The region experiences strong winds, frequent storms, and rapidly changing weather conditions, making it notorious among sailors and researchers alike. The passage is often subject to the effects of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current, which flows continuously around Antarctica, contributing to the choppy seas that define this area.
Weather patterns in the Drake Passage can shift dramatically within short periods, leading to conditions that can be both exhilarating and perilous. Sailors navigating these waters must be prepared for sudden squalls, towering waves, and dense fog. The unpredictable nature of the climate poses significant challenges for maritime operations, requiring vessels to be equipped with advanced navigational tools and experienced crews.
Understanding these weather patterns is essential for ensuring safety and efficiency in traversing this formidable passage.
The Challenge of Navigating Drake Passage
| Metrics | Data |
|---|---|
| Width of Drake Passage | 800 kilometers |
| Depth of Drake Passage | 4,000 meters |
| Strongest recorded winds | 113 miles per hour |
| Number of icebergs | Thousands |
| Duration of crossing | 2-3 days |
Navigating the Drake Passage is often described as one of the most daunting tasks for mariners due to its notorious reputation for rough seas and unpredictable weather. The combination of strong winds, powerful currents, and large swells creates an environment that can be both exhilarating and treacherous. Vessels traversing this passage must contend with waves that can reach heights of up to 15 meters (50 feet), making it imperative for crews to possess extensive experience and knowledge of the region.
The challenges posed by the Drake Passage extend beyond just physical navigation; they also encompass logistical considerations. The remoteness of the area means that assistance is often far away, requiring vessels to be self-sufficient in case of emergencies. Additionally, the passage’s proximity to Antarctica necessitates strict adherence to environmental regulations to protect fragile ecosystems.
As such, navigating the Drake Passage demands not only skillful seamanship but also a deep respect for the natural environment.
Unique Wildlife and Marine Life
The Drake Passage is home to an astonishing array of wildlife, making it a hotspot for marine biodiversity. The nutrient-rich waters support a variety of species, including krill, which serves as a fundamental food source for larger marine animals such as whales, seals, and seabirds. Among the notable inhabitants are humpback whales, orcas, and various species of penguins that thrive in this unique ecosystem.
The presence of these creatures highlights the ecological importance of the passage as a breeding ground and feeding area. Birdwatchers are particularly drawn to the Drake Passage due to its diverse avian population. Species such as albatrosses, petrels, and skuas can often be seen soaring above the waves or diving into the water in search of food.
The interplay between marine life and avian species creates a dynamic ecosystem that captivates researchers and nature enthusiasts alike. Efforts to study and protect these species are crucial for maintaining the delicate balance of life in this remarkable region.
Historical Significance and Exploration

The historical significance of the Drake Passage is deeply intertwined with maritime exploration and discovery. Sir Francis Drake’s voyage through these waters in 1578 marked one of the earliest European encounters with this remote region. His journey not only contributed to the mapping of uncharted territories but also paved the way for future explorers seeking to navigate the treacherous waters surrounding Antarctica.
Over the centuries, numerous expeditions have ventured into the Drake Passage, each contributing to our understanding of this challenging environment. Explorers such as Ernest Shackleton and Robert Falcon Scott faced incredible hardships while navigating these waters during their quests to reach Antarctica. Their stories of bravery and resilience continue to inspire modern adventurers who seek to follow in their footsteps.
The passage stands as a testament to human curiosity and determination in the face of nature’s formidable challenges.
Research and Scientific Discoveries
The Drake Passage has become a focal point for scientific research due to its unique ecological characteristics and its role in global ocean circulation. Researchers from around the world conduct studies in this region to better understand climate change, marine ecosystems, and oceanographic processes. The passage serves as a natural laboratory where scientists can observe interactions between different water masses and their impact on marine life.
One significant area of research involves studying the effects of climate change on ocean currents and temperatures in the Drake Passage. As global temperatures rise, understanding how these changes affect marine ecosystems becomes increasingly important. Additionally, researchers investigate the migration patterns of marine species, providing valuable insights into how environmental shifts influence biodiversity in this critical region.
The ongoing scientific endeavors in the Drake Passage contribute to a broader understanding of our planet’s health and resilience.
Environmental Concerns and Conservation Efforts
As awareness grows regarding environmental issues, the Drake Passage faces increasing scrutiny concerning its ecological health. Climate change poses significant threats to marine ecosystems, with rising temperatures affecting species distribution and abundance. Additionally, human activities such as shipping traffic and fishing practices raise concerns about overexploitation and habitat degradation.
Conservation efforts are underway to protect this vital region from further harm. Organizations dedicated to marine conservation work collaboratively with governments and researchers to establish protected areas within the Drake Passage. These initiatives aim to safeguard critical habitats while promoting sustainable practices among industries operating in or near these waters.
By prioritizing conservation efforts, stakeholders hope to ensure that future generations can continue to appreciate the unique beauty and biodiversity of the Drake Passage.
Tourism and Expedition Cruises
In recent years, tourism has emerged as a significant industry within the Drake Passage, with expedition cruises offering travelers an opportunity to experience its breathtaking landscapes and rich wildlife firsthand. These cruises attract adventurers eager to explore one of the last frontiers on Earth while providing educational experiences about the region’s ecology and history. Tour operators emphasize responsible tourism practices, ensuring that visitors minimize their impact on fragile ecosystems while enjoying their journeys through these waters.
Passengers often have opportunities to observe wildlife up close, participate in guided excursions on land, or engage in educational programs led by experts in marine biology and environmental science. This blend of adventure and education fosters a deeper appreciation for the natural world among travelers while supporting conservation efforts in the region.
The Role of Drake Passage in Global Ocean Circulation
The Drake Passage plays a pivotal role in global ocean circulation, acting as a conduit for water masses that influence climate patterns worldwide. The Antarctic Circumpolar Current flows through this passage, connecting the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans while facilitating heat exchange between these bodies of water. This current is essential for regulating global temperatures and distributing nutrients across vast oceanic regions.
Understanding the dynamics of ocean circulation within the Drake Passage is crucial for predicting climate change impacts on a global scale. Researchers study how variations in temperature and salinity affect current patterns, which can have far-reaching consequences for marine ecosystems and weather systems around the world. The passage’s significance extends beyond its immediate surroundings; it serves as a vital link in Earth’s interconnected oceanic systems.
Future Challenges and Opportunities in Drake Passage
Looking ahead, the Drake Passage faces both challenges and opportunities as environmental changes continue to unfold. Climate change remains a pressing concern, with potential impacts on marine biodiversity, weather patterns, and ocean circulation dynamics. As temperatures rise and ice melts in Antarctica, understanding how these changes will affect ecosystems within the passage becomes increasingly important.
However, there are also opportunities for collaboration among scientists, policymakers, and conservationists aimed at protecting this unique region. Increased awareness about environmental issues has led to greater advocacy for sustainable practices within industries operating in or near the Drake Passage. By fostering partnerships focused on research, conservation, and responsible tourism, stakeholders can work together to ensure that this remarkable body of water remains a source of wonder for generations to come.
Its unique geographical features, rich biodiversity, historical significance, and role in global ocean circulation make it an essential focus for understanding our planet’s health. As challenges arise from climate change and human activity, concerted efforts toward conservation will be vital in preserving this extraordinary region for future generations to explore and cherish.
The Drake Passage, a significant body of water located between the southern tip of South America and Antarctica, is renowned for its vastness and challenging conditions. Spanning approximately 800 kilometers (500 miles) wide, it serves as a crucial connector between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. For those interested in exploring more about the geographical features and significance of the Drake Passage, a related article can be found on MyGeoQuest. This article delves into the intricacies of the passage and its role in global ocean circulation. To learn more, visit the article on MyGeoQuest.
WATCH NOW! Drake Passage: Earth’s Deadliest Waters Revealed
FAQs
What is Drake Passage?
Drake Passage is the body of water between the southern tip of South America at Cape Horn and the South Shetland Islands of Antarctica. It connects the southwestern part of the Atlantic Ocean with the southeastern part of the Pacific Ocean.
How big is Drake Passage?
Drake Passage is approximately 500 miles (800 kilometers) wide. It is known for its rough seas and strong winds, making it one of the most challenging maritime routes in the world.
Why is Drake Passage significant?
Drake Passage is significant because it is the shortest and most direct route between Antarctica and the rest of the world. It also serves as a major gateway for the movement of ocean currents and marine life between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans.
What is the weather like in Drake Passage?
The weather in Drake Passage is characterized by strong winds, high waves, and rough seas. The area is notorious for its stormy conditions, which can make navigation and travel challenging.
Is Drake Passage important for scientific research?
Yes, Drake Passage is important for scientific research, particularly in the fields of oceanography, climatology, and marine biology. The unique oceanographic and atmospheric conditions in the passage make it an ideal location for studying the interactions between the Southern Ocean and the global climate system.
