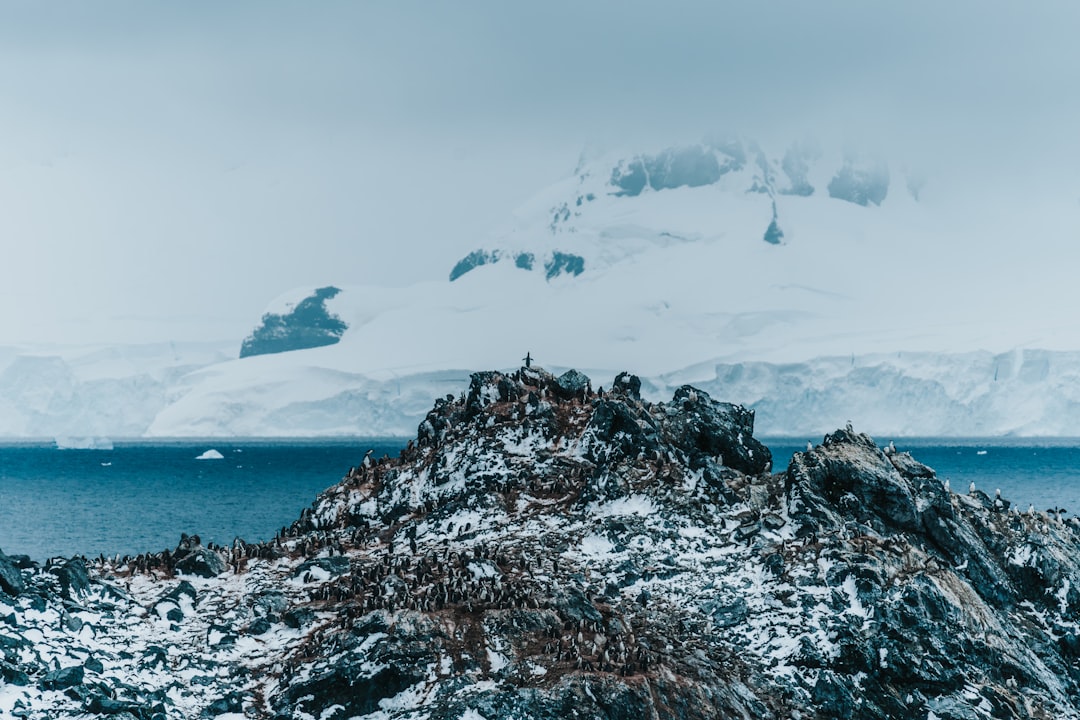
The Drake Passage, a body of water situated between the southern tip of South America and Antarctica, is renowned for its tumultuous seas and significant role in global oceanic circulation. This narrow stretch of ocean, measuring approximately 800 kilometers (500 miles) wide, serves as a critical conduit for the movement of water between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. Its unique geographical position not only makes it a vital area for marine biodiversity but also a focal point for maritime navigation and exploration.
The passage is often characterized by its unpredictable weather patterns and rough seas, which have earned it a reputation as one of the most challenging maritime routes in the world. The historical and scientific importance of the Drake Passage cannot be overstated. It has been a site of intrigue for explorers, scientists, and navigators alike, each drawn by the mysteries it holds beneath its turbulent surface.
The passage is not merely a geographical feature; it is a gateway to understanding the complex interactions between ocean currents, climate change, and marine ecosystems. As such, the Drake Passage stands as a testament to the enduring human spirit of exploration and the quest for knowledge about our planet’s oceans.
Key Takeaways
- Drake Passage is a narrow body of water between South America’s Cape Horn and the South Shetland Islands of Antarctica.
- Early explorers sought a southern sea route through the treacherous waters of the Southern Ocean, leading to the discovery of Drake Passage.
- Sir Francis Drake played a significant role in the exploration and naming of the passage during his circumnavigation of the globe in the late 16th century.
- Drake Passage is scientifically significant as it serves as a major gateway for the exchange of water, heat, and nutrients between the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans.
- Navigating Drake Passage presents significant challenges due to its notorious reputation for rough seas and strong winds, making it a critical area for conservation efforts and environmental protection.
Early Exploration of the Southern Ocean
The early exploration of the Southern Ocean, which encompasses the waters surrounding Antarctica, was fraught with peril and uncertainty. In the 16th and 17th centuries, European explorers set sail into these uncharted waters, driven by a desire for discovery and trade. Among them were notable figures such as Ferdinand Magellan and Sir Francis Drake, who ventured into the Southern Hemisphere in search of new trade routes and territories.
Their journeys were marked by treacherous conditions, including fierce storms and ice-laden waters, which tested their resolve and navigational skills. As these early explorers charted their courses through the Southern Ocean, they laid the groundwork for future expeditions. Their accounts of the harsh conditions and rich marine life sparked interest among scientists and adventurers alike.
The Southern Ocean became a symbol of both danger and opportunity, drawing individuals who sought to unlock its secrets. The challenges faced by these early explorers highlighted the need for better navigation techniques and a deeper understanding of oceanic phenomena, setting the stage for subsequent explorations in the region.
The Search for a Southern Sea Route
The quest for a southern sea route was driven by economic ambitions and geopolitical interests during the Age of Exploration. European powers sought to establish direct trade links with Asia, bypassing the overland routes that were fraught with obstacles. The allure of a passage that could connect the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans became a tantalizing goal for many explorers.
The Drake Passage emerged as a potential solution to this navigational challenge, promising a shortcut to lucrative markets. However, the search for this elusive route was not without its difficulties. Navigators faced formidable natural barriers, including icebergs, strong currents, and unpredictable weather patterns.
The Drake Passage itself became synonymous with perilous voyages, as many ships encountered violent storms that could easily capsize even the sturdiest vessels. Despite these challenges, the determination of explorers to find a southern sea route persisted, leading to numerous expeditions that would ultimately shape maritime history.
The Discovery of Drake Passage
| Year | Explorer | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| 1578 | Sir Francis Drake | First Englishman to navigate the passage |
| 1616 | Willem Schouten and Jacob Le Maire | First to successfully navigate the passage |
| 1833 | Charles Darwin | Scientific exploration of the area |
The formal recognition of the Drake Passage as a distinct geographical feature came about through the cumulative efforts of various explorers over several centuries. While Sir Francis Drake is often credited with its discovery during his circumnavigation of the globe in the late 16th century, it was not until later expeditions that its significance was fully understood. Drake’s journey through these waters provided valuable insights into the region’s geography and oceanic dynamics, paving the way for future exploration.
As explorers continued to navigate the passage in subsequent years, they began to document its unique characteristics. The realization that this narrow stretch of water played a crucial role in global ocean circulation emerged gradually. The Drake Passage became recognized not only as a navigational route but also as an area of scientific interest due to its influence on climate patterns and marine ecosystems.
This growing understanding marked a turning point in how explorers and scientists viewed the Southern Ocean and its interconnectedness with global systems.
The Role of Sir Francis Drake
Sir Francis Drake’s contributions to maritime exploration extend far beyond his famous circumnavigation of the globe; his role in navigating the waters that would later be named after him is particularly noteworthy. In 1578, during his expedition to circumnavigate the Earth, Drake sailed through what is now known as the Drake Passage. His journey was marked by both triumphs and tribulations, as he faced fierce storms and navigated treacherous waters that would later become infamous among sailors.
Drake’s exploration was not solely about discovery; it also had significant geopolitical implications. His successful voyage bolstered England’s naval power and established it as a formidable force on the global stage. By traversing the Drake Passage, he demonstrated that it was possible to navigate these challenging waters, inspiring future generations of explorers to undertake similar journeys.
His legacy endures not only in maritime history but also in the ongoing exploration of the Southern Ocean.
Scientific Significance of Drake Passage

The scientific significance of the Drake Passage lies in its role as a natural laboratory for studying oceanic processes and climate dynamics. The passage serves as a critical junction where cold Antarctic waters meet warmer currents from the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. This interaction creates unique conditions that support diverse marine ecosystems, making it an area of great interest for marine biologists and oceanographers alike.
Research conducted in the Drake Passage has revealed valuable insights into ocean circulation patterns and their impact on global climate systems. The passage plays a vital role in regulating heat distribution across the planet, influencing weather patterns far beyond its immediate vicinity. Scientists have utilized advanced technologies such as satellite imagery and underwater sensors to monitor changes in temperature, salinity, and marine life in this dynamic environment.
As climate change continues to pose challenges to marine ecosystems worldwide, understanding the intricacies of the Drake Passage becomes increasingly important.
Modern Exploration and Research in Drake Passage
In recent decades, modern exploration and research efforts in the Drake Passage have expanded significantly, driven by advancements in technology and a growing awareness of environmental issues. Research vessels equipped with sophisticated instruments now traverse these waters, collecting data on everything from ocean currents to marine biodiversity.
Collaborative international efforts have also emerged to study the ecological health of the Drake Passage and its surrounding regions. Scientists from various countries work together to monitor changes in marine populations, assess the impacts of climate change, and develop conservation strategies. The findings from these research initiatives contribute to a broader understanding of how human activities are affecting ocean ecosystems globally.
As interest in polar research continues to grow, the Drake Passage remains at the forefront of scientific inquiry.
Environmental Importance of Drake Passage
The environmental importance of the Drake Passage extends beyond its role as a navigational route; it is also a critical habitat for numerous marine species. The nutrient-rich waters support diverse ecosystems that include krill, fish, seals, and seabirds. These species are not only vital components of their respective food webs but also play essential roles in maintaining ecological balance within the Southern Ocean.
Moreover, the Drake Passage acts as a key player in global climate regulation. The exchange of water masses between different oceans influences heat distribution and contributes to weather patterns around the world. As climate change continues to alter ocean temperatures and currents, understanding how these changes affect marine life in the Drake Passage becomes increasingly crucial for conservation efforts.
Protecting this unique environment is essential not only for preserving biodiversity but also for maintaining global ecological health.
Challenges of Navigating Drake Passage
Navigating the Drake Passage presents numerous challenges that have historically deterred even experienced mariners. The passage is notorious for its unpredictable weather conditions, which can shift rapidly from calm seas to violent storms within minutes. High winds and large waves create treacherous sailing conditions that require skillful navigation and well-prepared vessels.
In addition to weather-related challenges, icebergs pose significant hazards for ships traversing these waters. The presence of floating ice can obstruct navigation routes and increase risks for vessels attempting to pass through the passage. Mariners must remain vigilant and employ advanced navigation techniques to safely navigate this perilous stretch of ocean.
Despite these challenges, many adventurers continue to brave the Drake Passage, drawn by its allure and promise of discovery.
Conservation Efforts in Drake Passage
Recognizing the ecological significance of the Drake Passage has led to increased conservation efforts aimed at protecting its unique marine environments. Various international organizations and governments have collaborated to establish marine protected areas (MPAs) within this region, aiming to safeguard critical habitats from overfishing and other human activities that threaten biodiversity. Conservation initiatives also focus on raising awareness about the importance of preserving marine ecosystems in the face of climate change.
Educational programs seek to engage local communities and promote sustainable practices that minimize environmental impact. By fostering a sense of stewardship among those who rely on these waters for their livelihoods or recreation, conservationists hope to ensure that future generations can continue to benefit from the rich resources found within the Drake Passage.
Future Implications of the Discovery of Drake Passage
The discovery of the Drake Passage has far-reaching implications for both maritime navigation and scientific research. As climate change continues to reshape oceanic landscapes worldwide, understanding how changes in this critical waterway affect global systems becomes increasingly vital. The passage serves as an indicator of broader environmental trends, providing valuable data that can inform policy decisions related to climate action.
Furthermore, ongoing research in the Drake Passage may yield insights into potential adaptations needed for marine species facing changing conditions. As scientists continue to explore this dynamic environment, they will undoubtedly uncover new knowledge that can contribute to conservation efforts both locally and globally. The legacy of exploration in the Drake Passage will continue to inspire future generations as they seek to unravel its mysteries while striving to protect its ecological integrity for years to come.
The Drake Passage, a significant body of water connecting the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans between the southern tip of South America and Antarctica, was first navigated by the English explorer Sir Francis Drake in the late 16th century. This discovery marked a pivotal moment in maritime history, opening new routes for exploration and trade. For those interested in learning more about the historical context and significance of this discovery, a related article can be found on MyGeoQuest. You can explore further details by visiting this link.
WATCH NOW! Drake Passage: Earth’s Deadliest Waters Revealed
FAQs
What is the Drake Passage?
The Drake Passage is a body of water located between the southern tip of South America and the northern tip of the Antarctic Peninsula. It connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean.
Who discovered the Drake Passage?
The Drake Passage is named after the English explorer Sir Francis Drake, who is credited with being the first European to navigate the passage in 1578. However, it is important to note that indigenous peoples of the region had likely been aware of the passage for centuries before Drake’s arrival.
How did Sir Francis Drake discover the passage?
Sir Francis Drake discovered the passage during his circumnavigation of the globe. He sailed through the treacherous waters of the passage in order to avoid the Spanish fleet and continue his journey.
Why is the Drake Passage significant?
The Drake Passage is significant because it is the shortest and most direct route between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans in the Southern Hemisphere. It is also known for its notoriously rough and unpredictable seas, making it a challenging and important route for maritime navigation.
